Ganymed SDK
Crypto API
Header file: usoc_crypto_API.h
It enables the access to the True-Random-Number-Generator (TRNG) in the Core. It allows the users to integrate randomly generated numbers into their applications. This only requires a function call to generate a variable number of randomly generated 32bit values.
usoc_trng_get_entropy
Acquires requested amount of entropy from the TRNG. This is a blocking access that can fail (if the TRNG is not in a secure state). The caller must always check the returned error code. The buffer needs to be created external and be able to contain the requested size.
usoc_trng_error_t usoc_trng_get_entropy(
uint32_t *data,
int32_t data_size
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| data | Pointer to a buffer of at least data_size |
| data_size | Amount of 32 bit words that should be read |
| return | 0 if the access succeeded, a suitable error code otherwise |
usoc_trng_error_t
The return value specifies, if the TRNG is in secure state.
typedef enum {
USOC_TRNG_ERR_NONE = 0,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_ILLEGAL_OP,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_READ_EMPTY,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_READ_FAIL,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_UNSECURE_STATE,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_MULTIPLE,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_SW_TIMEOUT,
USOC_TRNG_ERR_OTHER
} usoc_trng_error_t;| Error codes | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_NONE | No error |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_ILLEGAL_OP | Illegal operation |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_READ_EMPTY | Read data when no data available |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_READ_FAIL | Read data during TRNG failure / insecure state |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED | Read data of uninitialized TRNG |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_UNSECURE_STATE | TRNG not in secure state |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_MULTIPLE | Multiple errors |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_SW_TIMEOUT | Timeout while reading data |
| USOC_TRNG_ERR_OTHER | Undefined issue |
Interface API
Header file: usoc_interface_API.h
The data transfer via the interfaces is handled by the socket API. The interface API is used to start, configure and stop the interfaces. The API has access to the low level driver of the interfaces (ESP32 driver, TSN driver).
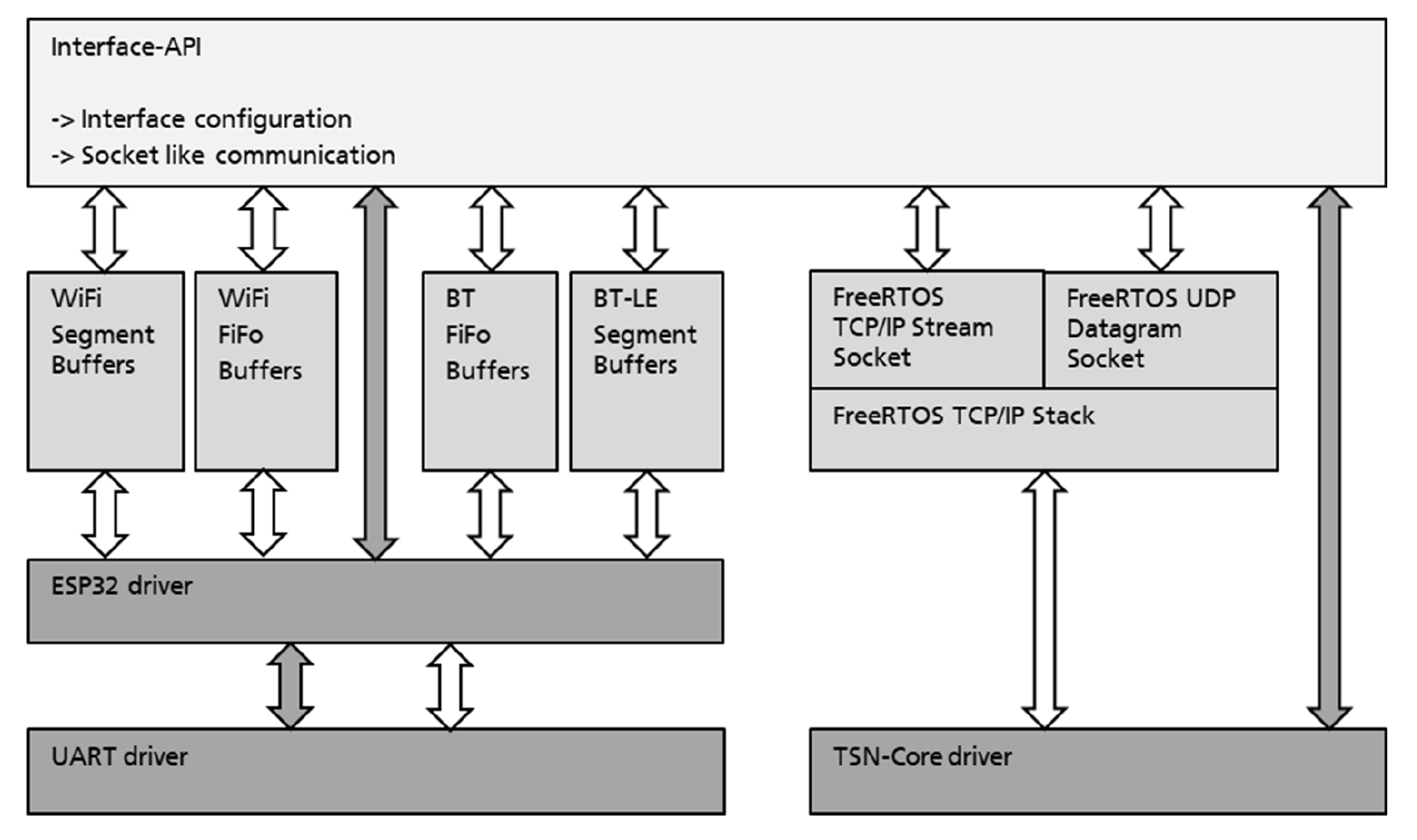
The usoc_interface_up function initializes an interface and starts it. The configuration for the interfaces is handled in the usoc_user_config_default.c. To de-initialize and shutdown the interface usoc_interface_down can be used. The interface API and socket API use components of FreeRTOS. It follows that the interface API can only be used with FreeRTOS.
The interface API and socket API are using components of FreeRTOS. Consequently, they can only be used together with FreeRTOS.
usoc_interface_t
Defines every available USoC interface.
typedef enum {
USOC_IFACE_LAN,
USOC_IFACE_WIFI,
USOC_IFACE_BT,
USOC_NMBR_OF_IFACE,
USOC_IFACE_CAN,
USOC_IFACE_BLE,
USOC_IFACE_UART
} usoc_interface_t;| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_IFACE_LAN | LAN |
| USOC_IFACE_WIFI | WLAN |
| USOC_IFACE_BT | Bluetooth |
| USOC_NMBR_OF_IFACE | The amount of interfaces that are supported by now |
| USOC_IFACE_CAN | Not supported for now |
| USOC_IFACE_BLE | Not supported for now |
| USOC_IFACE_UART | Not supported for now |
usoc_interface_error_t
Defines the error types which might be returned by the functions of the interface API.
typedef enum {
USOC_IFACE_ERR_NONE,
USOC_IFACE_ERR_ALREADY_UP,
USOC_IFACE_ERR_ALREADY_DOWN,
USOC_IFACE_ERR_ESP,
USOC_IFACE_ERR_CONFIG
} usoc_interface_error_t;| Error | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_IFACE_ERR_NONE | No error |
| USOC_IFACE_ERR_ALREADY_UP | Interface is already up |
| USOC_IFACE_ERR_ALREADY_DOWN | Interface is already down |
| USOC_IFACE_ERR_ESP | Error with the ESP32 |
| USOC_IFACE_ERR_CONFIG | Illegal configuration |
usoc_interface_up
Initializes the given interface. The function checks wether the interface is already up. If not so it initalizes RTOS and the ESP32 as well as interface specific ESP commands. Configuration parameter like ssid and pw for wifi can be changed in the global user config.
usoc_interface_error_t usoc_interface_up(
usoc_interface_t interface
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| interface | A communication interface from the enum usoc_interface_t |
| return | USOC_IFACE_ERR_NONE on success, a specific usoc_interface_error_t otherwise |
usoc_interface_down
Deininitalizes the given interface.
usoc_interface_error_t usoc_interface_down(
usoc_interface_t interface
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| interface | A communication interface from the enum usoc_interface_t |
| return | USOC_IFACE_ERR_NONE on success, a specific usoc_interface_error_t otherwise |
LAN Interface
Header file: usoc_interface_lan.h
usoc_lan_config_t
Holds the configuration options of a LAN interface.
typedef struct {
uint32_t mdio_clk;
uint8_t promisc_en;
uint8_t *mac;
uint8_t dhcp;
uint8_t *ip;
} usoc_lan_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| mdio_clk | MDIO clock speed |
| promisc_en | Whether promiscuous mode is enabled or not |
| mac | Pointer to an array of six unsigned 8 bit integer each representing a part of a MAC address |
| dhcp | Wether DHCP is used or not |
| ip | Pointer to an array of four unsigned 8 bit integer each representing a part of an IP address |
usoc_lan_config
Used to configure the LAN interface.usoc_interface_error_t usoc_lan_config(
usoc_interface_lock_t* lock,
usoc_interface_t interface,
usoc_lan_config_t* usoc_lan_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | |
| interface | |
| usoc_lan_config | usoc_lan_config_t |
Peripheral API
Header file: usoc_peripheral_API.h
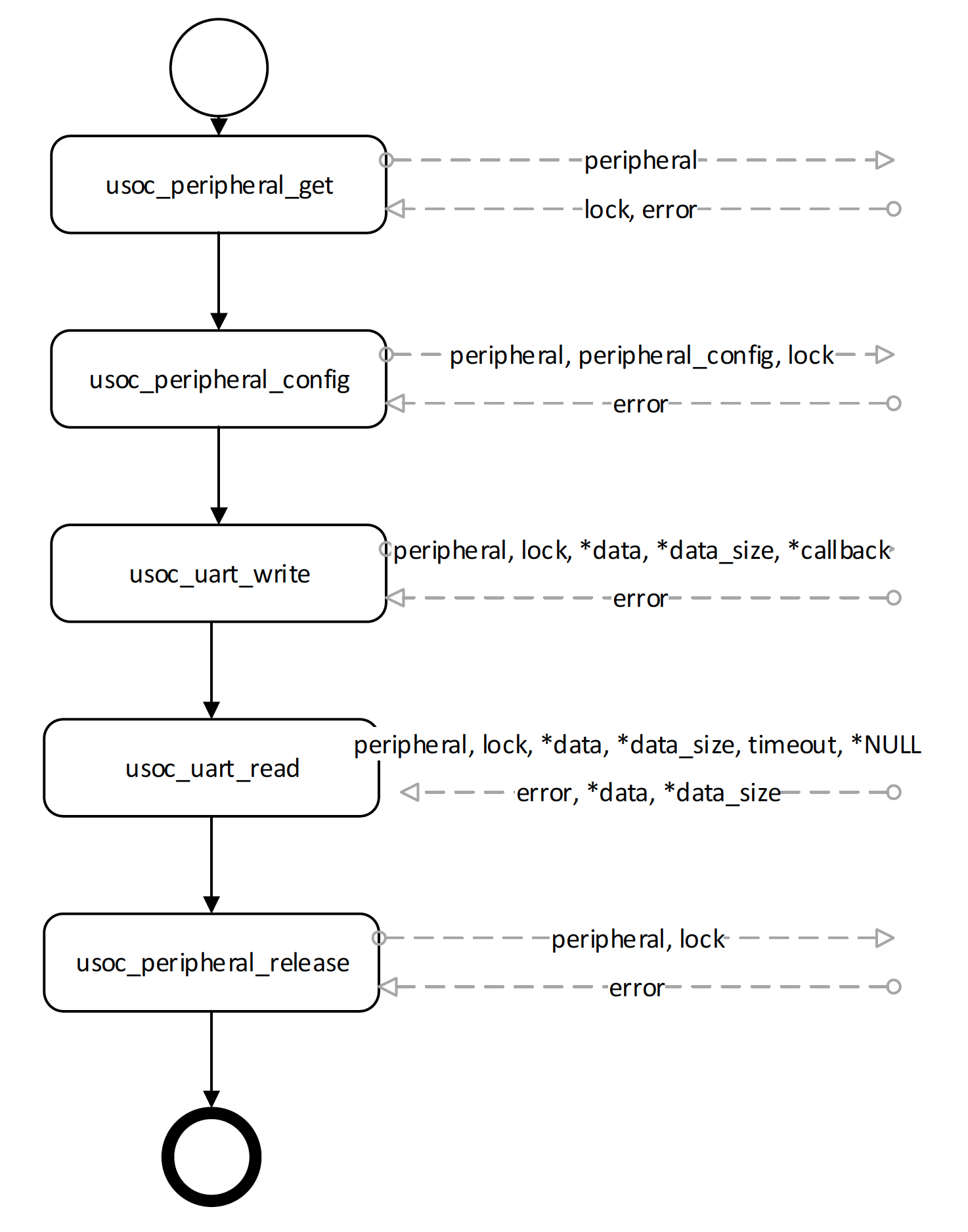
The following figure shows the typical usage of the peripheral API in blocking synchronous mode.
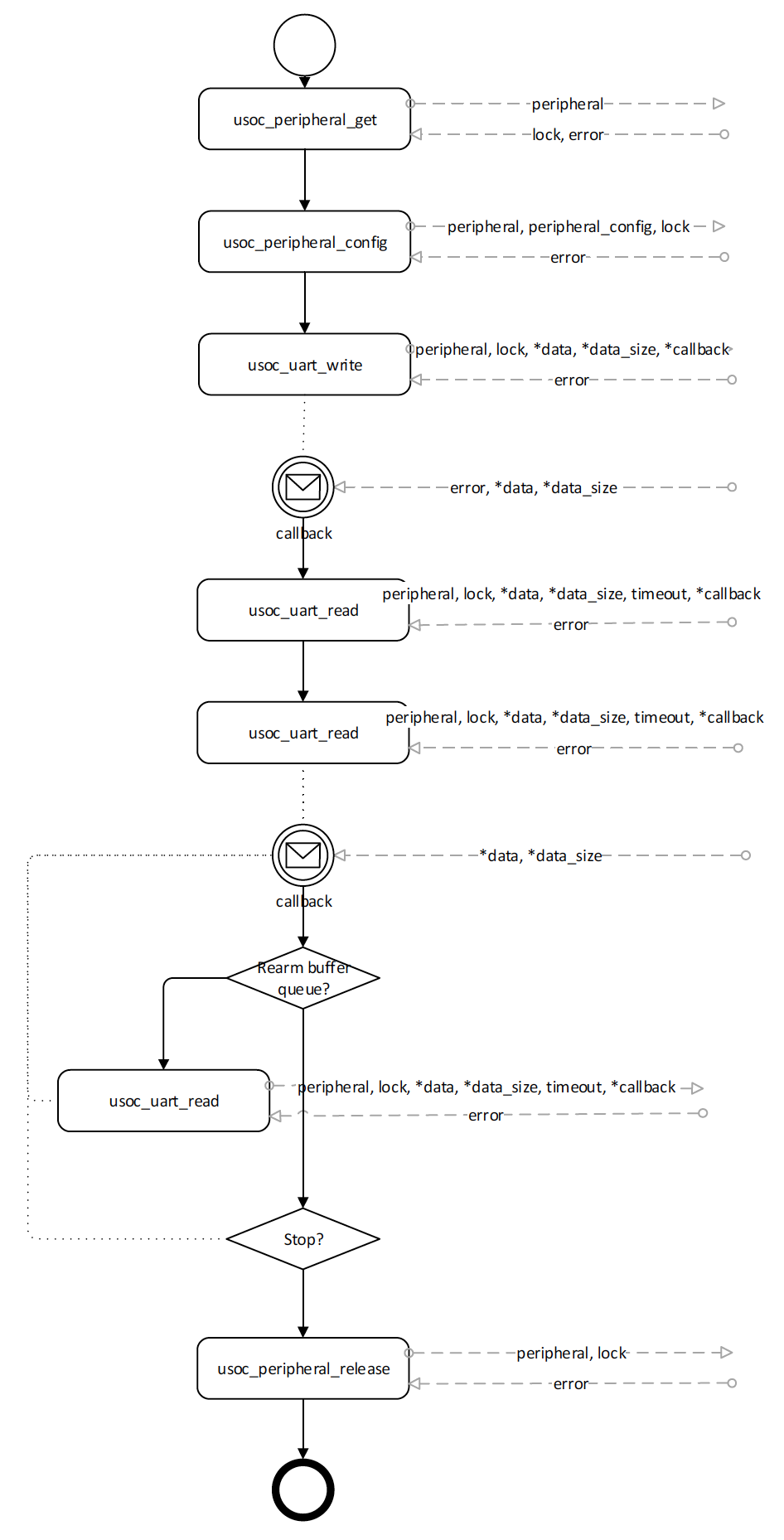
The following figure shows the typical usage of the peripheral API in non-blocking asynchronous mode.
usoc_peripheral_lock_t
Type definition for peripheral lock.
typedef uint32_t usoc_peripheral_lock_t;usoc_peripheral_t
There is a specific identifier for every single peripheral which is used within the API. This identifier is used by the API functions to distinguish on which peripheral to operate. The related function parameter is peripheral and valid values for this can be found in the following type.
typedef enum {
USOC_PER_UART0,
USOC_PER_UART1,
USOC_PER_UART2,
USOC_PER_SPI0,
USOC_PER_SPI1,
USOC_PER_SPI2,
USOC_PER_SPI3,
USOC_PER_SPI4,
USOC_PER_SPI5,
USOC_PER_SPI6,
USOC_PER_I2C0,
USOC_PER_I2C1,
USOC_PER_I2C2,
USOC_PER_I2C3,
USOC_PER_I2S0,
USOC_PER_I2S1,
USOC_PER_I2S2,
USOC_PER_I2S3,
USOC_PER_IO0,
USOC_PER_TIMER0,
USOC_PER_TSN0,
USOC_PER_CAN0,
USOC_NMBR_OF_PER
} usoc_peripheral_t;| Peripheral | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_PER_UART0 | UART interface no. 0 |
| USOC_PER_UART1 | UART interface no. 1 |
| USOC_PER_SPI0 | SPI interface no. 0 |
| USOC_PER_SPI1 | SPI interface no. 1 |
| USOC_PER_SPI2 | SPI interface no. 2 |
| USOC_PER_SPI3 | SPI interface no. 3 |
| USOC_PER_SPI4 | SPI interface no. 4 |
| USOC_PER_SPI5 | SPI interface no. 5 |
| USOC_PER_SPI6 | SPI interface no. 6 |
| USOC_PER_I2C0 | I2C interface no. 0 |
| USOC_PER_I2C1 | I2C interface no. 1 |
| USOC_PER_I2C2 | I2C interface no. 2 |
| USOC_PER_I2C3 | I2C interface no. 3 |
| USOC_PER_I2S0 | I2S interface no. 0 |
| USOC_PER_I2S1 | I2S interface no. 1 |
| USOC_PER_I2S2 | I2S interface no. 2 |
| USOC_PER_I2S3 | I2S interface no. 3 |
| USOC_PER_IO0 | IO interface no. 0 |
| USOC_PER_TIMER0 | Timer interface |
| USOC_PER_TSN0 | TSN interface no. 0 |
| USOC_PER_CAN0 | CAN interface no. 0 |
| USOC_NMBR_OF_PER | This is for determining the numbers elements within the enum definition |
USOC_PER_UART_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type UART.
#define USOC_PER_UART_MAX USOC_PER_UART2USOC_PER_SPI_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type SPI.
#define USOC_PER_SPI_MAX USOC_PER_SPI6USOC_PER_I2C_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type I2C.
#define USOC_PER_I2C_MAX USOC_PER_I2C3USOC_PER_I2S_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type I2S.
#define USOC_PER_I2S_MAX USOC_PER_I2S3USOC_PER_IO0_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type IO.
#define USOC_PER_IO0_MAX USOC_PER_IO0USOC_PER_TIMER_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type TIMER.
#define USOC_PER_TIMER_MAX USOC_PER_TIMER0USOC_PER_TSN_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type TSN.
#define USOC_PER_TSN_MAX USOC_PER_TSN0USOC_PER_CAN_MAX
Defines the last peripheral of type CAN.
#define USOC_PER_CAN_MAX USOC_PER_CAN0usoc_peripheral_error_t
The most peripheral functions include some error handling of type usoc_peripheral_error_t. For enumerations the first member holds the integer value zero. The following error codes are incremented.
typedef enum {
USOC_PER_ERR_NONE,
USOC_PER_ERR_PARAM,
USOC_PER_ERR_LOCK_FAIL,
USOC_PER_ERR_INTERNAL,
USOC_PER_ERR_EVENT_EMPTY,
USOC_PER_ERR_USER_EVENT,
USOC_PER_ERR_READY,
USOC_PER_ERR_ALLOC,
USOC_PER_ERR_NO_SUPPORT
} usoc_peripheral_error_t;| Error | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_PER_ERR_NONE | No error |
| USOC_PER_ERR_PARAM | Invalid parameter |
| USOC_PER_ERR_LOCK_FAIL | Locking failed |
| USOC_PER_ERR_LOCK_FAIL | Internal error |
| USOC_PER_ERR_EVENT_EMPTY | Event stack is empty |
| USOC_PER_ERR_USER_EVENT | User event stack is empty |
| USOC_PER_ERR_READY | Peripherie is not ready |
| USOC_PER_ERR_ALLOC | Allocation of memory failed |
| USOC_PER_ERR_NO_SUPPORT | Function call is not supported |
usoc_peripheral_get
To operate on a peripheral the user first needs to acquire a lock on the specific peripheral. On every subsequent operation on the peripheral the API is checking the validity of the lock. This is to avoid coterminous access by other tasks.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_peripheral_get(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_peripheral_release
If the user does not operate a peripheral anymore it can be released.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_peripheral_release(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_peripheral_config
After a lock to the peripheral was successfully acquired using the usoc_peripheral_get function the peripheral needs to be configured. If it is the first configuration call to the peripheral, the peripheral will automatically be opened. From now on, the peripheral can be reconfigured. To close a peripheral, for reason of power consumption, put a NULL to peripheral_config. As the configuration options differ between the peripheral types the peripheral_config is generic.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_peripheral_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
void *peripheral_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| peripheral_config | Pointer to generic configuration (usoc_xxx_config_t) structure, defined in usoc_peripheral_xxx.h, NULL pointer can be used to close the peripheral |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
No special configuration is required for the TIMER periphery type. No configuration is available. Calling usoc_peripheral_config with TIMER peripheral type will result in peripheral error.
CAN
Header file: usoc_peripheral_can.h
usoc_can_loopback_t
For testing purposes a loopback can be enabled, which sends the received messages back.
typedef enum {
CAN_LOOPBACK_NONE = (0x00),
CAN_LOOPBACK_INT = (0x01),
CAN_LOOPBACK_EXT = (0x02),
} usoc_can_loopback_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| CAN_LOOPBACK_NONE | Loopback mode disabled |
| CAN_LOOPBACK_INT | Internal loopback mode enabled |
| CAN_LOOPBACK_EXT | External loopback mode enabled |
usoc_can_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_can_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct {
usoc_can_loopback_t loopback;
uint8_t shutdown_en;
} usoc_can_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| loopback | Set loopback mode |
| shutdown_en | Enable the transceiver shutdown |
usoc_can_id_type_t
A CAN network can be configured to work with two different message formats and both are supported by Ganymed.
typedef enum {
CAN_ID_STD = (0x00),
CAN_ID_EXT = (0x01)
} usoc_can_id_type_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| CAN_ID_STD | Identifier in standard format |
| CAN_ID_EXT | Identifier in extended format |
usoc_can_rtr_t
Ganymed supports two different types of CAN frames. The data frame is the standard CAN message, broadcasting data from the transmitter to the other nodes on the bus. A remote frame is broadcast by a transmitter to request data from a specific node.
typedef enum {
CAN_RTR_DATA = (0x00),
CAN_RTR_REMOTE = (0x01)
} usoc_can_rtr_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| CAN_RTR_DATA | Data frame |
| CAN_RTR_REMOTE | Remote frame |
usoc_can_tx_header_t
Header format for a CAN frame.
typedef struct {
uint32_t id;
usoc_can_id_type_t id_type;
usoc_can_rtr_t rtr;
uint32_t len;
} usoc_can_tx_header_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| id | Specify the 11 bit standard identifier from 0 to 0x7FF or 29 bit extended identifier from 0 to 0x1FFFFFFF |
| id_type | Specify the identifier type |
| rtr | Specify the frame type |
| len | Specify the data length in bytes from 0 to 8 |
usoc_can_config
Open and configure the CAN peripherie.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_can_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_can_config_t* config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| config | Pointer to CANC configuration, use NULL pointer to close periphery |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_can_write
Send CAN-Frames via the CAN periphery.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_can_write(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_can_tx_header_t *header,
uint8_t *data,
void (*async_callback)(void*, uint32_t),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| header | Pointer to CAN message header |
| data | Pointer to message payload |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
The enumeration usoc_can_tx_header_t of the header defines the CAN message header.
usoc_can_read
Receive CAN-Frames packets from the CAN periphery.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_can_read(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t *data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*, uint32_t),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| data | Pointer to receive buffer |
| data_size | Pointer to received size variable |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
I2C
Header file: usoc_peripheral_i2c.h
usoc_i2c_pullup_mode_t
Holding the i2c pullup configuration.
typedef enum {
PULL_16k,
PULL_8k,
PULL_4k,
PULL_2k
} usoc_i2c_pullup_mode_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| PULL_16k | Pull up resistor 16k ohm |
| PULL_8k | Pull up resistor 8k ohm |
| PULL_4k | Pull up resistor 4k ohm |
| PULL_2k | Pull up resistor 2k ohm |
usoc_i2c_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_i2c_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct {
uint32_t bitrate;
usoc_i2c_pullup_mode_t pullup_mode;
} usoc_i2c_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| bitrate | Baudrate to be configured |
| pullup_mode | Pullup mode to be configured |
The parameter bitrate is issued as bits per second. The necessary dividers for the peripheral are calculated by the API itself based on the current clock settings of the SoC. Therefore the actual sample rate may be slightly lower than the issued one issued by the user depending on the viable divider settings. The pull up configuration can be selected by the following using the enumeration usoc_i2c_pullup_mode_t.
usoc_i2c_config
Open and configure the I2C peripherie.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_i2c_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_i2c_config_t *usoc_i2c_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| usoc_i2c_config | Pointer to I2C configuration, use NULL pointer to close peripherie |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_i2c_read
Receive data from the I2C periphery and store the bytes in *data buffer. It is possible to address I2C slave devices with sub addresses.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_i2c_read(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t address,
uint32_t iaddress,
uint8_t isize,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| address | 7-bit slave address |
| iaddress | Subaddress of slave device |
| isize | Size of subaddress in bytes, 0 if no subaddress is used |
| data | Pointer to the read buffer |
| data_size | Number bytes to read |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_i2c_write
Send data to the I2C periphery from the transmit buffer *data buffer. It is possible to address I2C slave devices with sub addresses.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_i2c_write(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t address,
uint32_t iaddress,
uint8_t isize,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| address | 7-bit slave address |
| iaddress | Subaddress of slave device |
| isize | Size of subaddress in bytes, 0 if no subaddress is used |
| data | Pointer to the write data |
| data_size | Size of the data in bytes |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
I2S
Header file: usoc_peripheral_i2s.h
usoc_i2s_width_t
Type holding i2s bit width.
typedef enum {
I2S_8_BIT,
I2S_16_BIT,
I2S_32_BIT
} usoc_i2s_width_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| I2S_8_BIT | 8 bit width |
| I2S_16_BIT | 16 bit width |
| I2S_32_BIT | 32 bit width |
usoc_i2s_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_i2s_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct {
uint32_t sample_rate;
usoc_i2s_width_t width;
} usoc_i2s_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| sample_rate | Sample rate in Hz, result in SCK frequency sck = sample_rate * width * 2 |
| width | Bit width of one sample |
The parameter sample_rate is issued as bits per second. The necessary dividers for the peripheral are calculated by the API itself based on the current clock settings of the SoC. Therefore the actual sample rate may be slightly lower than the issued one issued by the user depending on the viable divider settings. The sample width is addressed with the enumeration usoc_i2s_width_t.
usoc_i2s_config
Open and configure the I2S peripherie
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_i2s_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_i2s_config_t *usoc_i2s_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| usoc_i2s_config | Pointer to I2S configuration, use NULL pointer to close peripherie |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_i2s_capture
Receive data from the I2S periphery and store the bytes in *data buffer.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_i2s_capture(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| data | Pointer to read buffer |
| data_size | Number of bytes to read, should be multiple of i2s_config.width/8 |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
IO
Header file: usoc_peripheral_io_hi.h
usoc_io_config
Open and configure IO peripherie.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_io_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_io_config_t* io_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| usoc_io_config | Pointer to IO configuration, use NULL pointer to close peripherie |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_io_get_state
Read the current IO pin status from the periphery and store the mask of the pins state in *pin_state.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_io_get_state(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint32_t* pin_state
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| pin_state | Pointer to IO state |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_io_set_state
Write an IO pin configuration to periphery.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_io_set_state(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint32_t pin_state,
uint32_t pin_mask
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| pin_state | State of IO pins, if BIT0 is 1 then IO pin 0 is high |
| pin_mask | Mask of the pins, where pin_state are applied |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_io_interrupt_config
Enable the interrupts for IO pins. For IO interrupts there are callback functions required. These callback are called, if the interrupt event occurs. The event type can specified by usoc_io_interrupt_t.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_io_interrupt_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint32_t io_nmbr,
usoc_io_interrupt_t io_interrupt_type,
void (*interrupt_callback)(void*, uint32_t),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| io_nmbr | Number of IO pin |
| io_interrupt_type | Type of the interrupt, see usoc_io_interrupt_t |
| interrupt_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL not allowed |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
To unregister an interrupt callback issue NONE for io_interrupt_type_t or simply pass USOC_NULL for interrupt_callback.
usoc_io_pwm_enable
Enable PWM peripherals.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_io_pwm_enable(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t* lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint32_t io_nmbr,
uint32_t frequency,
uint32_t duty_cycle
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| io_nmbr | Number of IO pin |
| frequency | Frequency in Hz |
| duty_cycle | Fraction of one period in which the signal is active |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_io_pwm_disable
Disable PWM peripherals.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_io_pwm_disable(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t* lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint32_t io_nmbr
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| io_nmbr | Number of IO pin |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
Header file: usoc_peripheral_io_lo.h
usoc_io_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_io_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct{
uint32_t pin_mask; //!< defining the mask to be used for io operation
uint32_t pullup_enable; //!< defining on which pin to enable the internal pullup
uint32_t pulldown_enable; //!< defining on which pin to enable the internal pulldown
uint32_t is_output; //!< defining which pin is to be configured as output
} usoc_io_config_t;usoc_io_interrupt_t
Holding the interrupt configuration of a peripheral of the type IO
typedef enum{
NONE,
RISING_EDGE,
FALLING_EDGE,
HIGH_LEVEL,
LOW_LEVEL
} usoc_io_interrupt_t;SPI
Header file: usoc_peripheral_spi.h
usoc_spi_mode_t
Type holding spi mode.
typedef enum {
MODE_0,
MODE_1,
MODE_2,
MODE_3
} usoc_spi_mode_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MODE_0 | CPOL=0, CPHA=0 |
| MODE_1 | CPOL=0, CPHA=1 |
| MODE_2 | CPOL=1, CPHA=0 |
| MODE_3 | CPOL=1, CPHA=1 |
usoc_spi_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_spi_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct {
uint32_t bitrate;
usoc_spi_mode_t mode;
} usoc_spi_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| bitrate | Baudrate to be configured |
| mode | Mode to be configured |
The parameter bitrate is issued as bits per second. The necessary dividers for the peripheral are calculated by the API itself based on the current clock settings of the SoC. Therefore, the actual bitrate may be slightly lower than the issued one issued by the user depending on the viable divider settings. The SPI clock polarity and phase can be selected by the enumeration usoc_spi_mode_t.
usoc_spi_config
Open and configure the I2S peripherie.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_spi_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_spi_config_t *usoc_spi_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| usoc_spi_config | Pointer to SPI configuration, use NULL pointer to close peripherie |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_spi_readwrite
Send/receive data to/from the SPI periphery and store the received bytes to *rx_data buffer.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_spi_readwrite(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t cs_select,
uint8_t* tx_data,
uint8_t* rx_data,
uint32_t data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| cs_select | If 1 enable chip select |
| tx_data | Pointer to tx buffer |
| rx_data | Pointer to rx buffer |
| data_size | Number of bytes to transfer |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
Timer
Header file: usoc_peripheral_timer.h
usoc_timer_type_t
Holding the type of TIMER peripherie.
typedef enum {
TIMER_ONE_SHOT,
TIMER_PERIODIC
} usoc_timer_type_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| TIMER_ONE_SHOT | Timer in one shot mode |
| TIMER_PERIODIC | Timer in periodic mode |
usoc_timer_create
Create a new timer handle in periodic or oneshot mode.
usoc_timer_handle_t usoc_timer_create(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_timer_type_t type,
void (*async_callback)(void*),
void *arg,
usoc_peripheral_error_t *error
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| type | Type of timer usoc_timer_type_t |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| error | Pointer to usoc_peripheral_error_t to return error code |
| return | Timer instance handle if success, otherwise NULL |
There are two timer modes available which are defined in this enumeration usoc_timer_type_t. For TIMER periphery a callback function is required. The callback is called, if the time condition expires. The return value is the timer handle if successful created, otherwise NULL.
usoc_timer_start
If creating timer ends successful, it is possible to start timer with time value or stop the timer.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_timer_start(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t* lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_timer_handle_t handle,
uint32_t time_us
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| handle | Timer instance |
| time_us | Time delay/time period in micro seconds |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_timer_stop
Stop timer instance.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_timer_stop(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t* lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_timer_handle_t handle
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| handle | Timer instance |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_timer_destroy
If the timer is not needed anymore destroy it.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_timer_destroy(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t* lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_timer_handle_t handle
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| handle | Timer instance |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
TSN
Header file: usoc_peripheral_tsn.h
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a collection of standards, which enable low latency data tranmissions and high availability over ethernet networks. Possible usages are real time audo and data streams or real time control streams for cars, airplanes or industrial plants.
usoc_tsn_speed_t
This enum defines the supported speeds of the TSN connection.
typedef enum {
TSN_SPEED_1000,
TSN_SPEED_100,
TSN_SPEED_10
} usoc_tsn_speed_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| TSN_SPEED_1000 | 1000Mbit/s |
| TSN_SPEED_100 | 100Mbit/s |
| TSN_SPEED_10 | 10Mbit/s |
usoc_tsn_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_tsn_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct {
uint8_t enable;
usoc_tsn_speed_t speed;
uint8_t *mac;
uint8_t promisc_en;
} usoc_tsn_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| enable | Enable or disable core |
| speed | Speed of the tsn connection in usoc_tsn_speed_t format |
| mac | Pointer to an array containg six 8 bit integers each representing a part of a MAC address |
| promisc_en | Whether promiscuous mode is enabled or not |
For the TSN configuration it is possible to enable or disable the core, set the link speed, set the MAC address and enable the promiscuous mode. For the link speed the enumeration usoc_tsn_speed_t defines the allowed speeds.
usoc_tsn_tas_config_t
typedef struct {
uint32_t gate_state;
uint32_t time_interval_in_ms;
} usoc_tsn_tas_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| gate_state | |
| time_interval_in_ms | Time interval in ms |
usoc_tsn_timestamp_t
typedef struct {
uint32_t nsec;
uint32_t sec;
} usoc_tsn_timestamp_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| nsec | nanosecond fraction |
| sec | seconds |
usoc_tsn_tas_config
Is used to configure the time aware shaping.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_tsn_tas_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_tsn_tas_config_t* config,
uint8_t entry_count
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| config | usoc_tsn_tas_config_t |
| entry_count | |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
It takes a usoc_tsn_tas_config_t which can include multiple gate states and their corresponding time intervals.
Example for opening the gate for traffic queues 1 and 2.
usoc_tsn_tas_config_t tas_config[] = {{0x03, 499}};
usoc_peripheral_lock_t lock;
usoc_tsn_tas_config(&lock, USOC_PER_TSN0, tas_config, 1);usoc_tsn_write
Send Ethernet packets via the TSN periphery.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_tsn_write(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t data_size,
uint8_t tq,
void (*async_callback)(void*, uint32_t),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| data | Pointer to the binary data which should be send |
| data_size | Size of the binary data which should be send |
| tq | TSN traffic queue |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
The tq parameter select the TSN traffic queue. If the socket handling is enabled, this periphery is always locked by the Socket API and cannot used by users.
usoc_tsn_read
Receive Ethernet packets from the TSN periphery.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_tsn_read(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t *data_size,
usoc_tsn_timestamp_t *time,
void (*async_callback)(void*, uint32_t),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| data | Pointer to the recived binary data |
| data_size | Size of the recived binary data |
| time | Pointer to time in usoc_tsn_timestamp_t format |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
If the socket handling is enabled this periphery is always locked by the Socket API and cannot used by users.
UART
Header files: usoc_peripheral_uart.h
usoc_uart_stop_t
Type holding stop bit configuration. Stop bits are a time delay after the data bytes have been send.
typedef enum {
STOP_1,
STOP_1_5,
STOP_2
} usoc_uart_stop_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| STOP_1 | One bit delay |
| STOP_1_5 | One and a half bit delay |
| STOP_2 | Two bit delay |
usoc_uart_parity_t
Type holding parity configuration.
typedef enum {
PAR_NONE,
PAR_EVEN,
PAR_ODD,
PAR_MARK,
PAR_SPACE
} usoc_uart_parity_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| PAR_NONE | No pairty bit used |
| PAR_EVEN | The number of 1's in the data bit must have an even number of 1's including the parity bit. |
| PAR_ODD | The number of 1's in the data bit must have an odd number of 1's including the parity bit. |
| PAR_MARK | The pairty bit is always 1 |
| PAR_SPACE | The pairty bit is always 0 |
usoc_uart_config_t
A pointer to a structure of the type usoc_uart_config_t is used for generic peripheral configuration when calling the function usoc_peripheral_config.
typedef struct{
uint32_t baudrate;
usoc_uart_stop_t stopbits;
usoc_uart_parity_t parity;
uint32_t rx_timeout;
} usoc_uart_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| baudrate | Baudrate to be configured |
| stopbits | Stopbit configuration |
| parity | Parity configuration |
| rx_timeout | Receive timeout in milliseconds, 0 for blocking mode |
The parameter baudrate is issued as bits per second. The necessary dividers for the peripheral are calculated by the API itself based on the current clock settings of the SoC. Therefore the actual baudrate may be slightly lower than the issued one issued by the user depending on the viable divider settings. The other members are defined as enumerations usoc_uart_stop_t and usoc_uart_parity_t.
usoc_uart_config
Open and configure the UART peripherie.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_uart_config(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
usoc_uart_config_t *usoc_uart_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| usoc_uart_config | Config pointer to UART configuration, use NULL pointer to close peripherie |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_uart_read
Read from UART peripherie and store the received bytes to *data buffer.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_uart_read(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t *data,
uint32_t *data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*, uint32_t),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| data | Pointer to read buffer |
| data_size | Pointer to number of bytes to read |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
usoc_uart_write
Send data via the UART periphery from the transmit buffer *data of the size *data_size.
usoc_peripheral_error_t usoc_uart_write(
usoc_peripheral_lock_t *lock,
usoc_peripheral_t peripheral,
uint8_t* data,
uint32_t *data_size,
void (*async_callback)(void*),
void *arg
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| peripheral | Peripherie select from usoc_peripheral_t |
| data | Pointer data buffer |
| data_size | Pointer to number of bytes to write |
| async_callback | Pointer to callback function, NULL if blocking mode |
| arg | Pointer to user argument for callback function |
| return | usoc_peripheral_error_t |
Sensor API
Header file: usoc_sensor_API.h
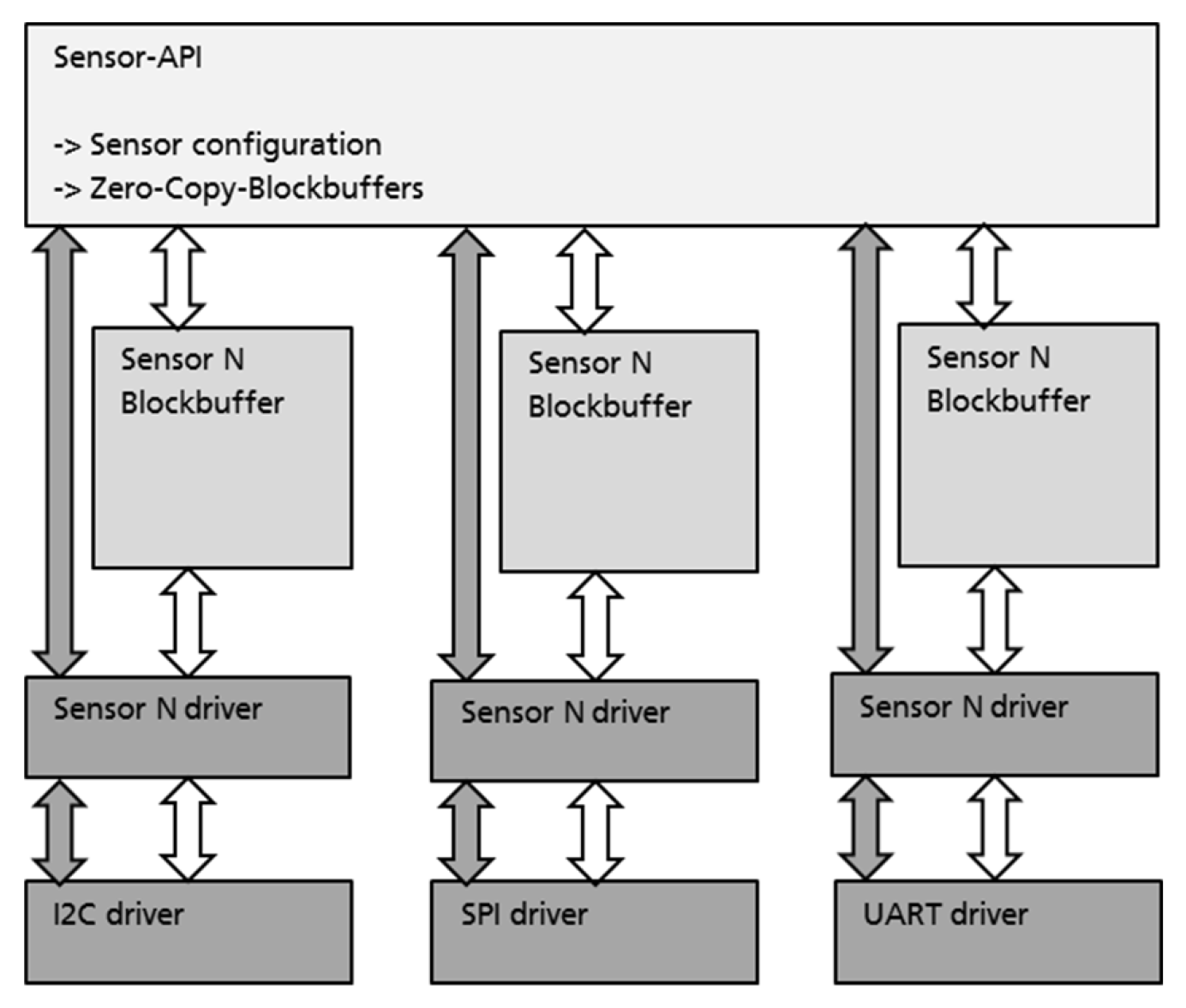
The Sensor-API will provide the user with a set of functions for simplified usage of the sensors included on L2 of the USoC and external sensors of L3. The user will first need to acquire a lock on the sensor. Subsequently the user will need to provide the Sensor-API with a user callback function and configure the blockbuffer to be used by the Sensor-API. The blockbuffer is an array of bufferblocks of the size n*sizeof(usoc_xxx_data_t). Hereby the actually used usoc_xxx_data_t depends on the sensor type.
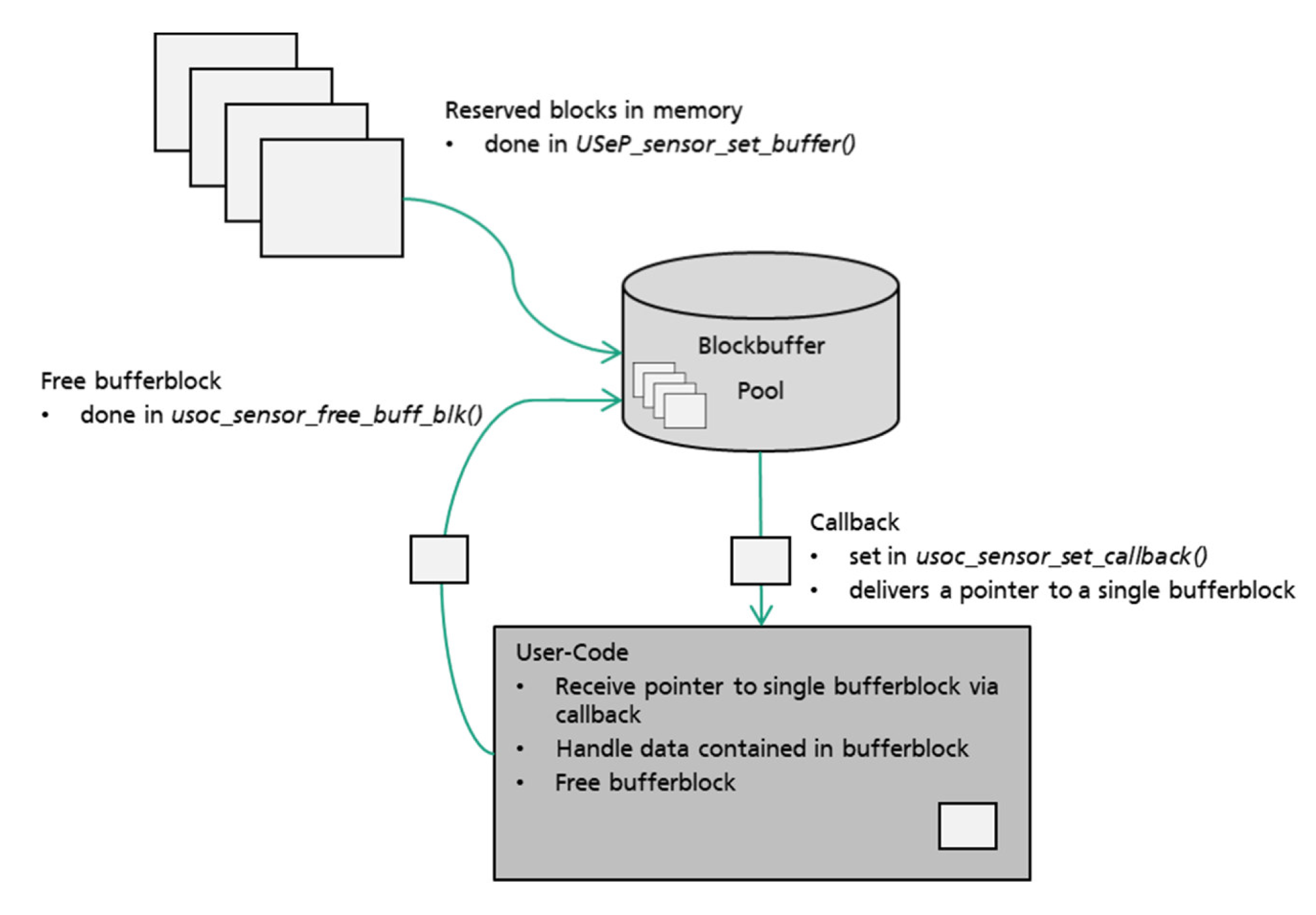
After the user set the sensor config via usoc_sensor_set_config and issues a usoc_sensor_start the Sensor-API starts collecting sensor data. After n sensor samples have been collected a single bufferblock will be filled with sensor data. The Sensor-API will internally switch to the next available bufferblock within the blockbuffer. A pointer to the filled bufferblock will be issued to the user-code using the previously configured callback and intend==USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_DATA. After the user-code finished its data processing and the data within the bufferblock is not needed anymore the user has to free the block by calling usoc_sensor_free_buff_blk. This will re-add the bufferblock to the blockbuffer pool for reuse. If there is no more free bufferblock the Sensor-API will dismiss sensor data until a bufferblock becomes available. The user will receive a sensor intent with intend==USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_ERROR_OVERRUN.
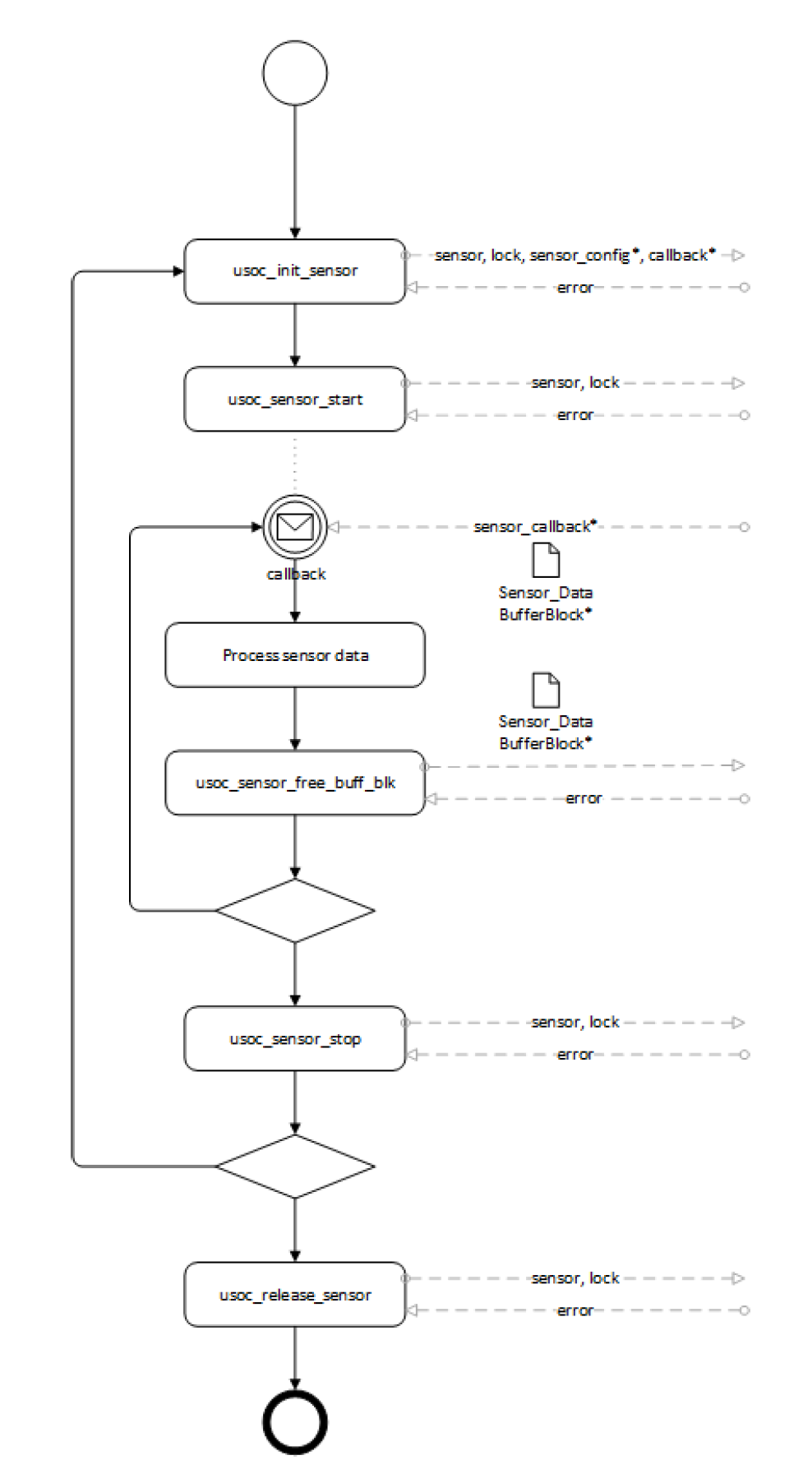
The following figure shows the typical usage of the sensor API.
usoc_sensor_t
The sensor api supports multiple sensors. This enum is used to select one of them.typedef enum {
USOC_SENSOR_L2_BME680,
USOC_SENSOR_L2_BMA456,
USOC_SENSOR_L2_MIS2DH,
USOC_SENSOR_L2_BMG250,
USOC_SENSOR_L3_MAX31865,
USOC_SENSOR_L3_ADIS16228CMLZ,
USOC_SENSOR_L3_CMP8270
} usoc_sensor_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_SENSOR_L2_BME680 | BME680 for measuring relative humidity, barometric pressure, ambient temperature and gas |
| USOC_SENSOR_L2_BMA456 | BMA456 for detecting wrist tilt, tab/double tab and enables plug 'n' play step counting especially in wearable devices |
| USOC_SENSOR_L2_MIS2DH | MIS2DH for measuring linear 3-dimensional acceleration |
| USOC_SENSOR_L3_MAX31865 | MAX31865 is an platinum resistance temperature detector |
| USOC_SENSOR_L3_ADIS16228CMLZ | ADIS16228CMLZ for measuring acceleration, tilt, shock, and vibration |
| USOC_SENSOR_L3_CMP8270 | CMP8270 for measuring pressure |
usoc_sensor_intent_type_t
A callback function is called when either new data is available or the buffer overran. This enum is used to decide between them.
typedef enum {
USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_DATA,
USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_ERROR_OVERRUN
} usoc_sensor_intent_type_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_DATA | New data available |
| USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_ERROR_OVERRUN | Buffer overrun |
usoc_sensor_intent_t
A callback function is called when either new data is available or the buffer overran, this struct is used as parameter for this callback function. The data block intent_data_ptr has to be released after usage with usoc_sensor_free_buff_blk
typedef struct
{
usoc_sensor_t sensor;
usoc_sensor_intent_type_t intent;
uint32_t size;
void *intent_data_ptr;
} usoc_sensor_intent_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| sensor | usoc_sensor_t |
| intent | usoc_sensor_intent_type_t |
| size | Data size |
| intent_data_ptr | intent_data_ptrData pointer |
usoc_init_sensor
Each sensor has to be initialized before it can be used.
usoc_sensor_error_t usoc_init_sensor(
usoc_sensor_t sensor,
usoc_sensor_lock_t *lock,
void *sensor_config,
void (*sensor_callback)(usoc_sensor_intent_t));| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sensor | usoc_sensor_t Type of sensor |
| lock | usoc_sensor_lock_t Pointer to socket configuration |
| sensor_config | Pointer to sensor configuration |
| sensor_callback | Pointer to callback function, which is called, |
| return | usoc_sensor_error_t |
The enumeration usoc_sensor_t defines the available sensors. It uses the usoc_sensor_intent_t. The sensor API function use some error handling defined in the enumeration usoc_sensor_error_t.
usoc_release_sensor
This function deininitalizes the sensor.usoc_sensor_error_t usoc_release_sensor(
usoc_sensor_t sensor,
usoc_sensor_lock_t *lock);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sensor | usoc_sensor_t Type of sensor |
| lock | usoc_sensor_lock_t Pointer to socket configuration |
| return | usoc_sensor_error_t |
The enumeration usoc_sensor_t defines the available sensors. The sensor API function use some error handling defined in the enumeration usoc_sensor_error_t.
usoc_sensor_start
This function starts the recoding of sensor data. The corresponding callback will be called when usoc_idle is called.
usoc_sensor_error_t usoc_sensor_start(
usoc_sensor_t sensor,
usoc_sensor_lock_t *lock);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sensor | usoc_sensor_t Type of sensor |
| lock | usoc_sensor_lock_t Pointer to socket configuration |
| return | usoc_sensor_error_t |
The enumeration usoc_sensor_t defines the available sensors. The sensor API function use some error handling defined in the enumeration usoc_sensor_error_t.
usoc_sensor_stop
This function stops the recoding of the sensor data. The callback will not be called anymore.
usoc_sensor_error_t usoc_sensor_stop(
usoc_sensor_t sensor,
usoc_sensor_lock_t *lock);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sensor | usoc_sensor_t Type of sensor |
| lock | usoc_sensor_lock_t Pointer to socket configuration |
| return | usoc_sensor_error_t |
The enumeration usoc_sensor_t defines the available sensors. The sensor API function use some error handling defined in the enumeration usoc_sensor_error_t.
usoc_sensor_free_buff_blk
After the callback function has been called, the data block intent_data_ptr has to be released with this function.
usoc_sensor_error_t usoc_sensor_free_buff_blk(
usoc_sensor_t sensor,
usoc_sensor_lock_t *lock,
void *intent_data_ptr);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sensor | usoc_sensor_t Type of sensor |
| lock | usoc_sensor_lock_t Pointer to socket configuration |
| intent_data_ptr | Pointer to sensor data |
| return | usoc_sensor_error_t |
The enumeration usoc_sensor_t defines the available sensors. The intent_data_ptr will point to a bufferblock of size*sizeof(usoc_xxx_data_t) in the case of intent==USOC_SENSOR_INTENT_DATA. The sensor API function use some error handling defined in the enumeration usoc_sensor_error_t.
SOC Control API
Header file: usoc_soc_control.h
The User SoC Control API is providing functions to control the SoC.
usoc_soc_clock_t
Ganymed supports multiple clock speeds.typedef enum {
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_100MHZ,
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_125MHZ,
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_200MHZ,
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_250MHZ,
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_333MHZ,
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_400MHZ,
USOC_SOC_CLOCK_500MHZ
} usoc_soc_clock_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_100MHZ | 100 MHz |
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_125MHZ | 125 MHz |
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_200MHZ | 200 MHz |
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_250MHZ | 250 MHz |
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_333MHZ | 333 MHz |
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_400MHZ | 400 MHz |
| USOC_SOC_CLOCK_500MHZ | 500 Mhz |
usoc_soc_clock
Set the USoC processor clock frequency by predefined divider settings. The clock divider values are defined by the hardware and depend on the PLL frequency of 2000 MHz. The default is 100 MHz.
void usoc_soc_clock(
usoc_soc_clock_t freq
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| freq | Frequency of SoC |
Socket API
Header file: usoc_socket.h
The configuration of the interfaces is handled by the Interface API. The socket API is used to create sockets, connect to server, listen as server, read data, write data and close sockets. The API has access to the low level driver of the interfaces (ESP32 driver, TSN driver).
The socket API and interface API use components of FreeRTOS. It follows that the socket API can only be used with FreeRTOS.
usoc_socket_t
typedef void* usoc_socket_t;usoc_sock_error_t
typedef enum {
USOC_SOCK_ERR_NONE,
USOC_SOCK_ERR_PARAM,
USOC_SOCK_ERR_MEM,
USOC_SOCK_ERR_INTERNAL
} usoc_sock_error_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_SOCK_ERR_NONE | No error |
| USOC_SOCK_ERR_PARAM | Function parameter error |
| USOC_SOCK_ERR_MEM | Memory allocation error |
| USOC_SOCK_ERR_INTERNAL | Error in lower driver API |
usoc_sock_domain_t
typedef enum {
USOC_INET_LAN,
USOC_INET_WIFI,
USOC_BT,
USOC_CAN,
USOC_UART
} usoc_sock_domain_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_INET_LAN | LAN |
| USOC_INET_WIFI | WIFI |
| USOC_BT | Bluetooth |
| USOC_CAN | CAN |
| USOC_UART | UART |
usoc_sock_protocol_t
typedef enum {
USOC_PROTO_TCP,
USOC_PROTO_UDP,
USOC_PROTO_NONE
} usoc_sock_protocol_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_PROTO_TCP | TCP protocol |
| USOC_PROTO_UDP | UDP protocol |
| USOC_PROTO_NONE | No protocol |
usoc_sock_type_t
typedef enum {
USOC_TYPE_STREAM,
} usoc_sock_type_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_TYPE_STREAM | usoc_sock_domain_t |
usoc_socket
Creates a new socket of a certain domain type usoc_sock_domain_t and allocates system resources for it.
usoc_socket_t usoc_socket(
usoc_sock_domain_t sock_domain,
usoc_sock_type_t sock_type,
usoc_sock_protocol_t sock_protocol
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sock_domain | Socket domain see: usoc_socket_domain_t |
| sock_type | Socket type see: usoc_socket_type_t |
| sock_protocol | Socket protocol see: usoc_socket_protocol_t |
| return | Socket handler, NULL if socket create failed |
For identification, the function returns a unique socket handle usoc_socket_t. The usoc_sock_protocol_t specifies the used protocol. Look at the following table for the allowed combinations of domain and protocol.
| Domain | PROTO_TCP | PROTO_UDP | PROTO_NONE |
|---|---|---|---|
| INET_LAN | ✓ | ✓ | x |
| INET_WIFI | ✓ | ✓ | x |
| BT | x | x | ✓ |
Note: Currently the socket type is not evaluated and is defined by the protocol type.
usoc_socket_connect
Makes the address information (e.g., IP address and port) of another socket known. Assigns a free local port to the socket. In case of a TCP or BT protocol it tries to establish a new connection.
usoc_sock_error_t usoc_socket_connect(
usoc_socket_t socket,
void* socket_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| socket_config | Pointer to socket configuration |
| return | usoc_sock_error_t |
A void pointer is handed for the connection information containing See the following table for the connection structures per domain.
| Connect structure | Description |
|---|---|
typedef struct { | Socket remote address string e.g. "192.168.0.59" Socket remote port e.g. 4660 |
typedef struct { | Socket remote address string e.g. "192.168.0.59" Socket remote port e.g. 4660 |
typedef struct { | Bluetooth remote address string e.g. "64:80:99:AD:F2:36" |
usoc_socket_bind
Binds the socket to a socket address information, usually an IP address and port. Typically used on the server side. Socket bind is only available for IP based protocol like TCP and UDP. Therefore the bind function is not supported if Bluetooth domain is used.
usoc_sock_error_t usoc_socket_bind(
usoc_socket_t socket,
void* socket_config
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| socket_config | Pointer to socket configuration |
| return | usoc_sock_error_t |
For the function a void pointer is handed for the bind information. See the following table for the bind structures per domain.
| Connect structure | Description |
|---|---|
typedef struct { | Local server port e.g. 4660 |
typedef struct { | Local server port e.g. 4660 Timeout after client sockets closed in seconds, 0 for no timeout |
typedef struct { | Bluetooth remote address string e.g. "64:80:99:AD:F2:36" |
usoc_socket_listen
Puts a socket into a listening mode. Used on the server side.
usoc_socket_t usoc_socket_listen(
usoc_socket_t socket
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| return | usoc_socket_t |
Returns a socket handle to the accepted socket.
usoc_socket_write
Write data to socket.
int32_t usoc_socket_write(
usoc_socket_t socket,
uint8_t* data,
uint32_t size,
void* flags
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| data | Pointer to data |
| size | Size of data in bytes |
| flags | unused |
| return | Number of successful written bytes, 0 if socket disconnect, -1 if failure |
usoc_socket_read
Read data from USoC Socket. It is a blocking function and blocks until data available or events are generated.
int32_t usoc_socket_read(
usoc_socket_t socket,
uint8_t* data,
uint32_t size,
void* flags
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| data | Pointer to data |
| size | Size of data in bytes |
| flags | Unused |
| return | Number of received bytes, 0 if socket disconnect, -1 if failure |
usoc_socket_close
Causes the operating system to release all resources allocated to the socket. If a TCP or BT domain is present, the connection is terminated.
usoc_sock_error_t usoc_socket_close(
usoc_socket_t socket
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| return | usoc_sock_error_t |
usoc_socket_get_local_port
uint32_t usoc_socket_get_local_port(
usoc_socket_t socket
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| socket | Socket handler |
| return | Port |
Storage API
Header file: usoc_storage_API.h
The Storage-API is providing functions for the user to store and load persistent data in the USoC memory.
usoc_storage_lock_t
Type definition for storage lock.
typedef uint32_t usoc_storage_lock_t;usoc_storage_t
Holding the identifiers for the usoc storage. There is a specific identifier for every single storage which is used within the API. This identifier is used by the API functions to distinguish on which peripheral to operate.
typedef enum {
USOC_STORE_MRAM,
USOC_STORE_SECURE_MRAM,
USOC_NMBR_OF_STORE
} usoc_storage_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_STORE_MRAM | MRAM |
| USOC_STORE_SECURE_MRAM | Secure MRAM |
| USOC_NMBR_OF_STORE | This is for determining the numbers elements within the enum definition |
usoc_storage_error_t
Holding the error types for the functions of the storage API.
typedef enum {
USOC_STORE_ERR_NONE,
USOC_STORE_ERR_PARAM,
USOC_STORE_ERR_LOCK_FAIL,
USOC_STORE_ERR_ALIGN,
USOC_STORE_ERR_READY
} usoc_storage_error_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| USOC_STORE_ERR_NONE | No error |
| USOC_STORE_ERR_PARAM | Function parameter error |
| USOC_STORE_ERR_LOCK_FAIL | Locking error |
| USOC_STORE_ERR_ALIGN | Internal error in memory alignment |
| USOC_STORE_ERR_READY | Storage is not ready |
The first member holds the integer value zero. The following error codes are incremented.
usoc_storage_get
Accquire lock for storage from storage API. To operate on a storage the user first needs to acquire a lock on the specific storage. On every subsequent operation on the storage the API is checking the validity of the lock. This is to avoid coterminous access by other tasks.
usoc_storage_error_t usoc_storage_get(
usoc_storage_lock_t* lock,
usoc_storage_t storage
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| storage | Storage select from usoc_storage_t |
| return | usoc_storage_error_t |
usoc_storage_release
If the user does not operate the storage anymore it can be released.
usoc_storage_error_t usoc_storage_release(
usoc_storage_lock_t* lock,
usoc_storage_t storage
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to the location where to store the lock |
| storage | Storage select from usoc_storage_t |
| return | usoc_storage_error_t |
MRAM
Header file: usoc_storage_mram.h
usoc_mram_read_word
Get one 32bit word from one of the MRAM memories at an offset within the MRAM memory. When reading the MRAM, the offset must be 32bit aligned.
usoc_storage_error_t usoc_mram_read_word(
usoc_storage_lock_t* lock,
usoc_storage_t storage,
uint32_t offset,
uint32_t* data_word
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to lock variable |
| storage | Type of storage peripherie |
| offset | Offset in MRAM, must be 32bit aligned |
| data_word | Pointer to data word |
| return | usoc_storage_error_t |
usoc_mram_write_word
Write one 64bit double word to MRAM storage. The hardware requires a 64bit aligned offset. So writing is only possible for double words (64 bit). Access to unaligned offsets and incompatible data types must be handled by user software.
usoc_storage_error_t usoc_mram_write_word(
usoc_storage_lock_t* lock,
usoc_storage_t storage,
uint32_t offset,
uint64_t data_dword
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| lock | Pointer to lock variable |
| storage | Type of storage peripherie |
| offset | Offset in MRAM, must be 64bit aligned |
| data_dword | Double word write data |
| return | usoc_storage_error_t |
User Services
Header file: usoc_user_services.h
usoc_log_level
The Ganymed SDK specifies three log levels.
typedef enum {
ERROR = 0x00,
INFO = 0x01,
DEBUG = 0x02
} usoc_log_level;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ERROR | Error level |
| INFO | Info level |
| DEBUG | Debug level |
usoc_api_log
For a pretty log output this function can be used by the user and it is used internally. It complies the given log level.
void usoc_api_log(
usoc_log_level logLevel,
char *file,
uint32_t line,
const char *message,
...
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| logLevel | usoc_log_level |
| file | Filename |
| line | Line number |
| message | Message in printf style |
| ... | Additional arguments in printf style |
usoc_sprintf
USoC sprintf function to convert formatted strings to string.
int usoc_sprintf(
char *str,
const char *format,
...
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| str | String buffer to store converted string |
| format | Formatted string |
| ... | List format arguments |
| return | Number of bytes in string buffer |
usoc_printf
Can be used to print strings or formatted strings with arguments via the debug interface. For the USoC the default debug output is UART0 with a baudrate of 230400 bit/s.
void usoc_printf(
const char *format,
...
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| format | Formatted string |
| ... | List format arguments |
usoc_idle
If using asynchronous function calls it is required to call the usoc_idle occasionally. This will request waiting callbacks from kernel and execute them in user mode.
void usoc_idle();usoc_time_get_us
Can be used to get a current system time. The return value is the time in microseconds after booting the system. The resolution of the system time depends on the used timer clock.
uint32_t usoc_time_get_us();| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| return | The current time in microseconds |
usoc_time_delay_us
Can be used to block the processing for a given amount of microseconds. Can be called from user space.
void usoc_time_delay_us(
uint32_t us
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| us | Delay in microseconds |
usoc_exit
Exit the user application.
void usoc_exit(
int status
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| status | Status code |
usoc_user_alloc
Can be used by the user to allocate dynamic memory. It reserve a memory area of size bytes from the user heap and return the pointer to the memory block. The size of the user heap is defined in the user linker script.
void *usoc_user_alloc(
int size
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| size | Number of bytes to allocate |
| return | NULL, if no space available, otherwise th pointer to memory block |
usoc_user_free
Free a memory block.
void usoc_user_free(
void *chunk,
int size
);| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| chunk | Pointer to memory block |
| size | Size of memory block in bytes |
ADIS16228
Header file: usoc_sensor_ADIS16228_public.h
usoc_ADIS16228_data_t
The device specific data format for the ADIS16228 holds three 16 bit values for X-, Y- and Z-Axis vibration values.
typedef struct {
int16_t x __attribute__((packed));
int16_t y __attribute__((packed));
int16_t z __attribute__((packed));
} usoc_ADIS16228_data_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| x | X-axis sensor data |
| y | Y-axis sensor data |
| z | Z-axis sensor data |
usoc_ADIS16228_mode_t
typedef enum {
ADIS16228_MANUAL_MODE = 0x00,
ADIS16228_MANUAL_FFT_MODE = 0x01
} usoc_ADIS16228_mode_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ADIS16228_MANUAL_MODE | Manual mode |
| ADIS16228_MANUAL_FFT_MODE | Fast Fourier transform mode |
usoc_ADIS16228_power_mode_t
typedef enum {
ADIS16228_MODE_NORMAL = 0x00,
ADIS16228_MODE_LOW_POWER = 0x01
} usoc_ADIS16228_power_mode_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ADIS16228_MODE_NORMAL | Normal mode |
| ADIS16228_MODE_LOW_POWER | Low power mode |
usoc_ADIS16228_range_t
#define ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_1g 0x01
#define ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_5g 0x05
#define ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_10g 0x0A
#define ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_20g 0x14
typedef enum {
ADIS16228_RANGE_1G = ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_1g,
ADIS16228_RANGE_5G = ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_5g,
ADIS16228_RANGE_10G = ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_10g,
ADIS16228_RANGE_20G = ADIS16228_FULL_SCALE_20g
} usoc_ADIS16228_range_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ADIS16228_RANGE_1G | 1g range |
| ADIS16228_RANGE_5G | 5g range |
| ADIS16228_RANGE_10G | 10g range |
| ADIS16228_RANGE_20G | 20g range |
usoc_ADIS16228_config_t
The device specific sensor configuration for the ADIS16228 vibration sensor.
typedef struct {
usoc_ADIS16228_power_mode_t power_mode;
usoc_ADIS16228_mode_t mode;
usoc_ADIS16228_range_t range;
uint32_t block_count;
} usoc_ADIS16228_config_t;
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| power_mode | usoc_ADIS16228_power_mode_t |
| mode | usoc_ADIS16228_mode_t |
| range | usoc_ADIS16228_range_t |
| block_count |
BME680
Header file: usoc_sensor_BME680_public.h
usoc_BME680_oversampling_t
typedef enum {
BME680_OVERSAMPLING_OFF = 0x00,
BME680_OVERSAMPLING_1X = 0x01,
BME680_OVERSAMPLING_2X = 0x02,
BME680_OVERSAMPLING_4X = 0x03,
BME680_OVERSAMPLING_8X = 0x04,
BME680_OVERSAMPLING_16X = 0x05
} usoc_BME680_oversampling_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| BME680_OVERSAMPLING_OFF | No oversampling |
| BME680_OVERSAMPLING_1X | One time oversampling |
| BME680_OVERSAMPLING_2X | Two times oversampling |
| BME680_OVERSAMPLING_4X | Four times oversampling |
| BME680_OVERSAMPLING_8X | Eight times oversampling |
| BME680_OVERSAMPLING_16X | Sixteen times oversampling |
usoc_BME680_filter_t
![X_filt[n] = (X_filt[n-1] * (c - 1) + x_ADC)/(c)](/BME680-formula.png)
Xfilt[n - 1] is the data which is coming from the current filter memory while XADC is the data which is coming from current ADC acquisition. Xfilt[n] denotes the new value of filter memory and the value that will be sent to the output registers. The IIR filter can be configured with different filter coefficients to reduce noise. Note that the response time with enabled IIR filter will slow down depending on the number of samples generated. This means that the data output rate must be known to calculate the actual response time.
typedef enum {
BME680_FILTER_0 = 0x00,
BME680_FILTER_1 = 0x01,
BME680_FILTER_3 = 0x02,
BME680_FILTER_7 = 0x03,
BME680_FILTER_15 = 0x04,
BME680_FILTER_31 = 0x05,
BME680_FILTER_63 = 0x06,
BME680_FILTER_127 = 0x07
} usoc_BME680_filter_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| BME680_FILTER_0 | Set c to 0 |
| BME680_FILTER_1 | Set c to 1 |
| BME680_FILTER_3 | Set c to 3 |
| BME680_FILTER_7 | Set c to 7 |
| BME680_FILTER_15 | Set c to 15 |
| BME680_FILTER_31 | Set c to 31 |
| BME680_FILTER_63 | Set c to 63 |
| BME680_FILTER_127 | Set c to 127 |
usoc_BME680_data_t
typedef struct {
int32_t t __attribute__((packed));
int32_t p __attribute__((packed));
int32_t h __attribute__((packed));
int32_t g __attribute__((packed));
} usoc_BME680_data_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| t | Temperature |
| p | Pressure |
| h | Humidity |
| g | Raw gas quality |
usoc_BME680_config_t
The device specific sensor configuration for the BME680 gas sensor measuring relative humidity, barometric pressure, ambient temperature and gas (VOC).
typedef struct {
usoc_BME680_oversampling_t oversampling_t;
usoc_BME680_oversampling_t oversampling_p;
usoc_BME680_oversampling_t oversampling_h;
usoc_BME680_filter_t filter_tp;
// usoc_BME680_gas_heater_temperature_t heater_temperature;
// usoc_BME680_gas_heater_duration_t heater_waiting_time;
uint32_t values_per_block;
uint32_t block_count;
} usoc_BME680_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| oversampling_t | usoc_BME680_oversampling_t oversampling for temperature |
| oversampling_p | usoc_BME680_oversampling_t oversampling for pressure |
| oversampling_h | usoc_BME680_oversampling_t oversampling for humidity |
| filter_tp | usoc_BME680_filter_t |
| heater_temperature | Unused |
| heater_waiting_time | Unused |
| values_per_block | |
| block_count |
CMP8270
Header file: usoc_sensor_CMP8270_public.h
usoc_CMP8270_data_t
typedef struct{
int16_t pressure __attribute__((packed));
} usoc_CMP8270_data_t;The device specific data format for the CMP holds a 16 bit pressure value.
usoc_CMP8270_config_t
typedef struct{
uint32_t values_per_block;
uint32_t block_count;
} usoc_CMP8270_config_t;BMG250
Header file: usoc_sensor_BMG250_public.h
usoc_BMG250_output_rate_t
#define BMG250_ODR_25HZ 0x06
#define BMG250_ODR_50HZ 0x07
#define BMG250_ODR_100HZ 0x08
#define BMG250_ODR_200HZ 0x09
#define BMG250_ODR_400HZ 0x0A
#define BMG250_ODR_800HZ 0x0B
#define BMG250_ODR_1600HZ 0x0C
#define BMG250_ODR_3200HZ 0x0D
typedef enum {
BMG250_RATE_25HZ = BMG250_ODR_25HZ,
BMG250_RATE_50HZ = BMG250_ODR_50HZ,
BMG250_RATE_100HZ = BMG250_ODR_100HZ,
BMG250_RATE_200HZ = BMG250_ODR_200HZ,
BMG250_RATE_400HZ = BMG250_ODR_400HZ,
BMG250_RATE_800HZ = BMG250_ODR_800HZ,
BMG250_RATE_1600HZ = BMG250_ODR_1600HZ,
BMG250_RATE_3200HZ = BMG250_ODR_3200HZ
} usoc_BMG250_output_rate_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| BMG250_RATE_25HZ | 25Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_50HZ | 50Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_100HZ | 100Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_200HZ | 200Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_400HZ | 400Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_800HZ | 800Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_1600HZ | 1600Hz |
| BMG250_RATE_3200HZ | 3200Hz |
usoc_BMG250_range_t
DPS = Degree per seconds
#define BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_2000_DPS 0x00
#define BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_1000_DPS 0x01
#define BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_500_DPS 0x02
#define BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_250_DPS 0x03
#define BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_125_DPS 0x04
typedef enum {
BMG250_RANGE_2000_DPS = BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_2000_DPS,
BMG250_RANGE_1000_DPS = BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_1000_DPS,
BMG250_RANGE_500_DPS = BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_500_DPS,
BMG250_RANGE_250_DPS = BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_250_DPS,
BMG250_RANGE_125_DPS = BMG250_GYRO_RANGE_125_DPS
} usoc_BMG250_range_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| BMG250_RANGE_2000_DPS | 2000 DPS |
| BMG250_RANGE_1000_DPS | 1000 DPS |
| BMG250_RANGE_500_DPS | 500 DPS |
| BMG250_RANGE_250_DPS | 250 DPS |
| BMG250_RANGE_125_DPS | 125 DPS |
usoc_BMG250_filter_t
#define BMG250_BW_OSR4_MODE 0x00
#define BMG250_BW_OSR2_MODE 0x01
#define BMG250_BW_NORMAL_MODE 0x02
typedef enum {
BMG250_FILTER_NORMAL = BMG250_BW_NORMAL_MODE,
BMG250_FILTER_OSR2 = BMG250_BW_OSR2_MODE,
BMG250_FILTER_OSR4 = BMG250_BW_OSR4_MODE
} usoc_BMG250_filter_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| BMG250_FILTER_NORMAL | No oversampling |
| BMG250_FILTER_OSR2 | Two times oversampling |
| BMG250_FILTER_OSR4 | Four times oversampling |
usoc_BMG250_power_mode_t
This structure holds the information of power mode.
#define BMG250_GYRO_SUSPEND_MODE 0x14
#define BMG250_GYRO_NORMAL_MODE 0x15
#define BMG250_GYRO_FASTSTARTUP_MODE 0x17
typedef enum {
BMG250_MODE_NORMAL = BMG250_GYRO_NORMAL_MODE,
BMG250_MODE_FAST_STARTUP = BMG250_GYRO_FASTSTARTUP_MODE
} usoc_BMG250_power_mode_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| BMG250_MODE_NORMAL | Normal mode |
| BMG250_MODE_FAST_STARTUP | Fast startup mode |
usoc_BMG250_offset_t
Bmg250 offset structure.
typedef struct {
uint16_t x_offset;
uint16_t y_offset;
uint16_t z_offset;
} usoc_BMG250_offset_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| x_offset | X offset |
| y_offset | Y offset |
| z_offset | Z offset |
usoc_BMG250_data_t
The device specific data format for the BMG250 hold three 16 bit values for X-, Y- and Z-Axis gyroscope values.
typedef struct{
int16_t x __attribute__((packed));
int16_t y __attribute__((packed));
int16_t z __attribute__((packed));
} usoc_BMG250_data_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| x | X-axis sensor data |
| y | Y-axis sensor data |
| z | Z-axis sensor data |
usoc_BMG250_config_t
The device specific sensor configuration for the BMG250 gyroscope sensor.
typedef struct {
usoc_BMG250_power_mode_t power_mode;
usoc_BMG250_output_rate_t output_rate;
usoc_BMG250_range_t range;
usoc_BMG250_filter_t filter;
usoc_BMG250_offset_t offset;
uint32_t values_per_block;
uint32_t block_count;
} usoc_BMG250_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| power_mode | usoc_BMG250_power_mode_t |
| output_rate | usoc_BMG250_output_rate_t |
| range | usoc_BMG250_range_t |
| filter | usoc_BMG250_filter_t |
| offset | usoc_BMG250_offset_t |
| values_per_block | |
| block_count |
MAX31865
Header file: usoc_sensor_MAX31865_public.h
usoc_MAX31865_filter_t
typedef enum {
MAX31865_FILTER_50HZ,
MAX31865_FILTER_60HZ
} usoc_MAX31865_filter_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MAX31865_FILTER_50HZ | |
| MAX31865_FILTER_60HZ |
usoc_MAX31865_wire_t
typedef enum {
MAX31865_WIRE_3,
MAX31865_WIRE_2_4
} usoc_MAX31865_wire_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MAX31865_WIRE_3 | |
| MAX31865_WIRE_2_4 |
usoc_MAX31865_data_t
typedef uint16_t usoc_MAX31865_data_t;The device specific data format for the MAX31865 holds a 16 bit temperature value.
usoc_MAX31865_config_t
The device specific sensor configuration for the MAX31865 temperature sensor.
typedef struct {
uint32_t sample_period;
usoc_MAX31865_filter_t filter;
usoc_MAX31865_wire_t wire;
uint32_t block_count;
} usoc_MAX31865_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| sample_period | Sample rate in ms, minimum of 65ms |
| filter | usoc_MAX31865_filter_t |
| wire | usoc_MAX31865_wire_t |
| block_count | Number of buffer with one data set |
MIS2DH
Header file: usoc_sensor_MIS2DH_public.h
usoc_MIS2DH_power_mode_t
The MIS2DH provides three different operating modes which are high-resolution mode, normal mode and low-power mode. They will affect the resolution of the output.
typedef enum {
MIS2DH_MODE_NORMAL = 0x02,
MIS2DH_MODE_LOW_POWER = 0x01,
MIS2DH_MODE_HIGH_RESOLUTION = 0x03
} usoc_MIS2DH_power_mode_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MIS2DH_MODE_NORMAL | 10-bit data output |
| MIS2DH_MODE_LOW_POWER | 8-bit data output |
| MIS2DH_MODE_HIGH_RESOLUTION | 12-bit data output |
usoc_MIS2DH_range_t
The MIS2DH provides four measurement ranges.
#define MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_2g 0x00
#define MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_4g 0x01
#define MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_8g 0x02
#define MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_16g 0x03
typedef enum {
MIS2DH_RANGE_2G = MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_2g,
MIS2DH_RANGE_4G = MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_4g,
MIS2DH_RANGE_8G = MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_8g,
MIS2DH_RANGE_16G = MIS2DH_FULL_SCALE_16g
} usoc_MIS2DH_range_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MIS2DH_RANGE_2G | ±2.0g |
| MIS2DH_RANGE_4G | ±4.0g |
| MIS2DH_RANGE_8G | ±8.0g |
| MIS2DH_RANGE_16G | ±16.0g |
usoc_MIS2DH_output_rate_t
The MIS2DH offers multiple output rates for acceleration measurement. The output rates 1620Hz and 5376Hz require low power mode to work, while 1344Hz is not supported for low power mode.
typedef enum {
MIS2DH_RATE_1HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_10HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_25HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_50HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_100HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_200HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_400HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_1344HZ,
MIS2DH_RATE_1620HZ_LP,
MIS2DH_RATE_5376HZ_LP,
} usoc_MIS2DH_output_rate_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MIS2DH_RATE_1HZ | 1Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_10HZ | 10Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_25HZ | 25Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_50HZ | 50Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_100HZ | 100Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_200HZ | 200Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_400HZ | 400Hz |
| MIS2DH_RATE_1344HZ | 1344Hz not available with low power mode |
| MIS2DH_RATE_1620HZ_LP | 1620Hz only available with low power mode |
| MIS2DH_RATE_5376HZ_LP | 5376Hz only available with low power mode |
usoc_MIS2DH_filter_t
The MIS2DH offers a high-pass filter which depending on the selected output data rate and on the settings of the filter itself.
#define MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_00 0x00
#define MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_01 0x01
#define MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_10 0x02
#define MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_11 0x03
typedef enum {
MIS2DH_FILTER_NONE = 0xFF,
MIS2DH_FILTER_0 = MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_00,
MIS2DH_FILTER_1 = MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_01,
MIS2DH_FILTER_2 = MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_10,
MIS2DH_FILTER_3 = MIS2DH_FILTER_FREQ_11
} usoc_MIS2DH_filter_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| MIS2DH_FILTER_NONE | |
| MIS2DH_FILTER_0 | |
| MIS2DH_FILTER_1 | |
| MIS2DH_FILTER_2 | |
| MIS2DH_FILTER_3 |
usoc_MIS2DH_data_t
The device specific data format for the MIS2DH offers three values for X-, Y- and Z-Axis acceleration. The bit depth of these values depends on the operation mode. 8, 10 and 12bit values are possible, which are packed into a 16bit value.
typedef struct {
int16_t x __attribute__((packed));
int16_t y __attribute__((packed));
int16_t z __attribute__((packed));
} usoc_MIS2DH_data_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| x | X-Axis acceleration |
| y | Y-Axis acceleration |
| z | Z-Axis acceleration |
usoc_MIS2DH_config_t
The device specific sensor configuration for the MIS2DH acceleration sensor.
typedef struct{
usoc_MIS2DH_power_mode_t power_mode;
usoc_MIS2DH_output_rate_t output_rate;
usoc_MIS2DH_range_t range;
usoc_MIS2DH_filter_t filter;
uint32_t values_per_block;
uint32_t block_count;
} usoc_MIS2DH_config_t;| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| power_mode | usoc_MIS2DH_power_mode_t |
| output_rate | usoc_MIS2DH_output_rate_t |
| range | usoc_MIS2DH_range_t |
| filter | usoc_MIS2DH_filter_t |
| values_per_block | |
| block_count |
